Search engine optimization. Something we know like the back of our hand! With us, you’ll have the opportunity to work with experts who have a wealth of experience. We are here for you if you want help with strategy, content and outreach. Let us help you rank high!
Technical SEO
Technical search engine optimization (SEO) means optimizing and ensuring that a website is technically sound and has the right conditions to rank high. The right conditions can mean, for example, that the website is visible to search engines, that there is a good structure on the page or that there are fast loading times. We recommend that you ensure your technical SEO before starting work on content and other areas that search engine optimization includes.
Indexing in search engines
Today there are a number of different search engines, with Google being the undisputed leader. Examples of other search engines are Bing and Yahoo, which together account for 4% of all searches – small compared to Google’s 93%. Regardless of market share, these three search engines work more or less the same way. By automatically visiting and storing information about websites, they create an index. This is called ‘crawling’ or ‘spidering’. A website that has never been spidered by Google can never appear in their search results.
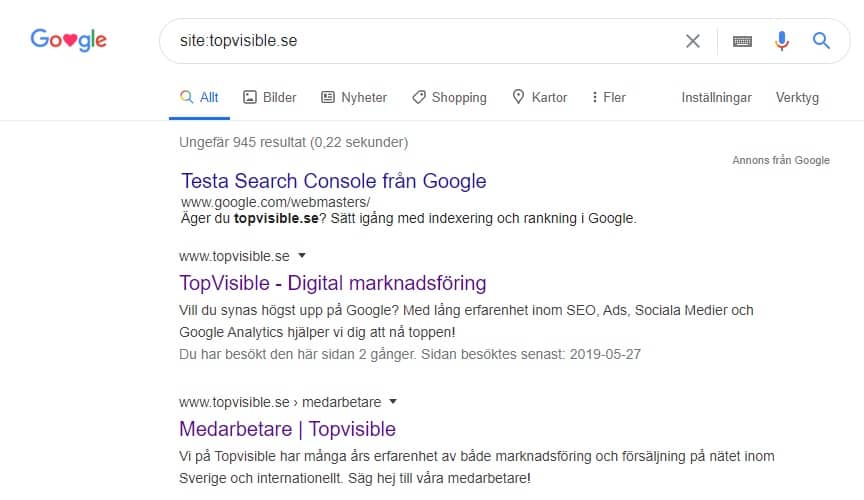
You can see which pages on your website are indexed by typing “site:” followed by your domain in Google like the example below.
We can see that our domain has 681 pages indexed on Google, this figure may be incorrect and show +- some pages wrong. To be sure how many pages are really indexed, we refer you to Google Search Console.
Robots.txt
Robots.txt is a way to control what content search engines should have access to. Robots.txt allows you to prevent Google or other search engines from indexing specific pages on your website. It is important that the file does not block important pages or javascript files. The file should also include a reference to one or more sitemaps.
For examples, you can access our robots.txt here: topvisible.se/robots.txt
HTTP Status Codes
HTTP response codes are status codes given to the visitor or search engine when they visit the page. These 3-digit codes represent a status of your website. It may happen that pages that have been removed are still indexed and have visitors trying to access the page. In this case, the visitor is returned with a 404 response code stating that the page they are trying to visit no longer exists.
For web owners who remove a page on their site, it is important to redirect potential traffic that the page receives to another page. This can be done with the 301 and 302 status codes. It is important to keep track of the status codes present on a website, as Google can choose to index, de-index or update information about a page based on these codes. Review 301, 302, 404 and 500.
We recommend the Screaming Frog tool!
Page speed
Short loading times mean quality, and quality is something Google really wants to deliver. A study conducted in 2017 showed that 53% of visitors leave a page if it takes more than 3 seconds to load. Optimizing load times is thus something that is important when it comes to technical SEO.
Check your loading times with Google’s own Google PageSpeed Insights tool!
The tool provides you with information on how your website performs in terms of speed – on mobile and desktop. It also provides you with a concrete action list. A common reason for slow websites is images. It’s easy to include large and beautiful images with good quality. The problem is that the web page becomes very large and requires a fast connection to load quickly, which many visitors do not have. A simple solution is to compress images and use the .jpg file format instead of .png
Mobile-friendly website
Having a mobile-friendly website has never been more important. Google has been increasingly vocal over the years about the importance of websites optimized for mobile users. Especially after the number of mobile users took over the top spot as the main user group. Google has also implemented mobile-first indexing. This means that Google uses the mobile version of a website, instead of the desktop version, when indexing a website.
As there is a significant difference in the size of a computer screen versus a mobile screen, it is important that the content of websites adapts to the screen size. Websites that adapt in this way are often called responsive websites or responsive design.
Like speed, you can check if your website is mobile-friendly by using Google’s Mobile Friendliness Test.
SSL certificate
Google categorizes websites into two categories, secure and non-secure. Being categorized as a secure website by Google is achieved through SSL Certificates. The certificate ensures that traffic to and from the site is encrypted. Sites with SSL certificates get a lock in the browser, the lock indicates that it is a secure site.
Sites without a valid SSL certificate are presented as non-secure, and Google advises visitors not to provide any sensitive information.
Canonical Links
A canonical link is a small snippet of code that tells Google which address to index in cases where there may be more than one. If a website has two pages with similar content, Google will choose to add only one of the pages to its index. That page will then be representative of the content. The other page is then seen as a duplicate. If your website suffers from this problem, you can see it on Google Search Console, under “Review URL”.
platform
The platform is an important aspect to consider if you want an SEO-friendly site. Think about what the goal of your website is and then choose a CMS adapted to your needs. Do you have an information-based website or an e-commerce site? Should you use WordPress, Magento or Drupal?
URL addresses
Whether URLs help to rank pages higher is difficult to say. Regardless, it is important to optimize them, as URLs are one of the few elements that Google presents in its search results. Like the Title and Description, the URL is a visual component that should help draw in visitors.
The recommendation is that the URL should clearly declare what it is about. Best practice is to include important keywords in the URL. On our website, for example, you can read about SEO under https://www.topvisible.se/seo/. This makes it clear to both Google and visitors what the page is about. In the search results, the page’s URL is presented with so-called “breadcrumbs”.
In addition to having a clear structure of the URLs, it is recommended to have a reasonable length of them. They should not be too long but not too short either. This of course depends from page to page. In the example above, it would be unnecessary to make it longer.
XML Sitemap
An XML sitemap is a map of all pages on the website. You have this for the search engines – so they can index the site better and not risk missing any pages. The sitemap should normally be available at https://www.topvisible.se/sitemap.xml. It should also be submitted to Google and Bing, and linked to in the robots.txt file.
Structured data
In technical SEO, Structured Data can play an important role, giving you an edge over your competitors. If you structure the content in your website’s code, Google can in turn give you increased results in search results. This is often referred to as ‘Rich Results’ or ‘Rich Snippets’. There are different types of extended results a webpage can get, a common example is the “Featured Snippet”. The featured snippet gives the website “position zero” on Google search results, above all other competitors.
Structured data is usually implemented using Schema.org. In our guide to Structured Data we explain everything about the topic. We give an in-depth answer to what Structured Data is, and how to implement it on your site.
We also help you with:
Structured Data
Fill your search results with (even) more valuable content.